7.4 Raster Processing Toolset
For this chapter, you will need the following R Packages:
library(arc2r)
library(raster)
library(sf)
library(dplyr)
library(stars)7.4.1 Clip Raster
In GIS operations is quite common the necessity of “clipping” an area based on some specific region of interest. This is a quite useful and necessary procedure not only when we are dealing with vector datasets, but also when we have to work with raster ones. In ArcGIS pro the procedure of “cutting” a portion of a raster dataset, mosaic dataset, or an image service layer is performed using Clip Raster tool. In R, the respective operation can be performed using the mask() function. For the example below, we are using the following datasets:
- ARE_waedi: Vector dataset that depicts the public transport connection quality in the city of Wädenswil
- raster_recycling: Dataset derived from the spatial interpolation of all the available “recycling points”in the city of Wädenwil
# Insert a vector dataset that depicts the public transport connection quality in
# the city of Wädenswil and plot it
data("are_waedenswil")
# Read the raster dataset and plot it
data("recycling_raster")Plot the two datasets one over the other.
plot(recycling_raster)
plot(are_waedenswil, alpha = 0.5, add = TRUE)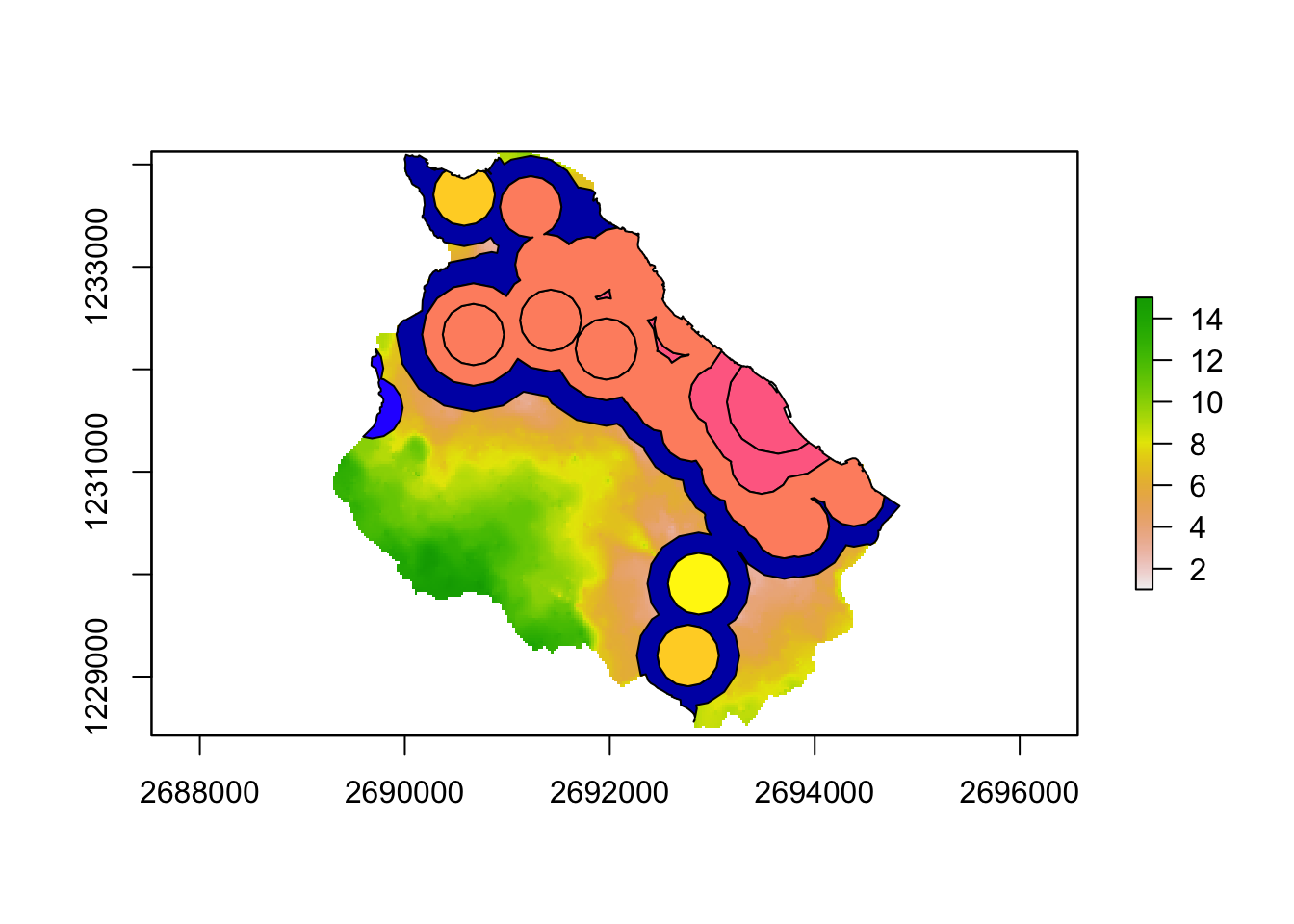
In our case, the vector dataset serves as the clipping extent for the clipping operation.
recycle_Waedi_clip <- mask(recycling_raster, are_waedenswil)Visualising the clipped output
plot(recycle_Waedi_clip)